implementation of skid steer kinematic model In order to asses the performance of the proposed kinematic model for dead reckoning scenarios indoor tests on a marble surface and outdoor tests both on . See more Gehlmax-IHI 25 NX is a mini excavator manufactured from 2001 to 2005, with a weight of 2.68 tons. It features a track width of 300 mm, a transport length of 3.94 meters, a transport width of 1.5 meters, and a transport height of 2.46 meters.
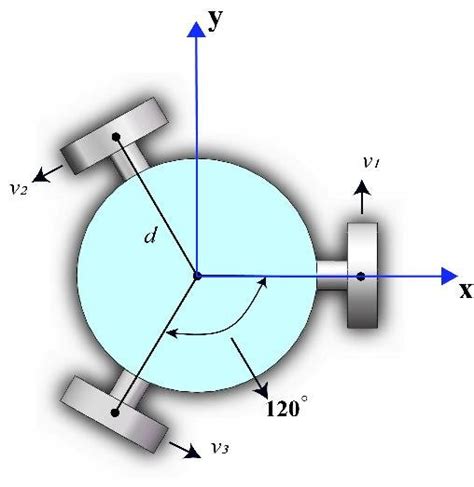
0 · wheeled kinematic model
1 · kinematic model for wheeled platform
2 · 4 wheel skid steering robot
A: To dig a trench with a mini excavator, position the machine correctly, adjust the blade and bucket angles to the desired depth, drive forward to excavate, and manage the excavated soil to maintain a clean and stable .
wheeled kinematic model
2011 cat skid steer 289c
Figure 6 shows a summary of the tests done on marble surface with a symmetric mass distribution. The robot was driven using the speed pairs shown on Fig. 6a, corresponding to the whole motion range of the robot. Figure 6b shows the rotational speed of the robot measured with the IMU as well as the ones . See moreThe kinematic model was validated by adding weights sequentially either to the back (Figs. 4a, 5b, c), or to the sides of the robots (Figs. 4b, 5a), shifting the . See moreIn order to verify the assumption that wheels with more traction have minimum skid steer slip values (\(\Sigma _{SS}\)) Eq. 1 was calculated for the back wheels and . See moreIn order to asses the performance of the proposed kinematic model for dead reckoning scenarios indoor tests on a marble surface and outdoor tests both on . See more
It combines detailed slip and terramechanic-based dynamic models of .
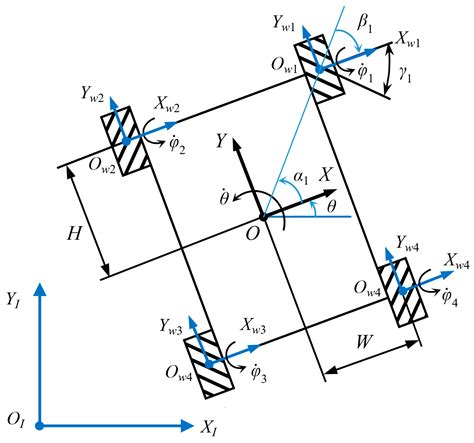
In this section kinematic and dynamic model of four-wheel skid-steering mobile robot is .This paper presents a kinematic extended Kalman filter (EKF) designed to estimate the .This methodology performs online calibration of vehicle kinematic models via Extended Kalman . In this paper, we develop an analysis and experimental kinematic scheme for a .
A survey and comparison of previous work on kinematic models for skid-steer mobile robots. .
Based on the analysis of the kinematics of the skid-steered mobile robot, the . This article describes an improved kinematic model that takes these factors into account and verifies the model in a variety of working conditions, including different terrains and asymmetric loads, for two different wheeled skid-steered platforms. It combines detailed slip and terramechanic-based dynamic models of wheel–terrain interaction with online learning via Extended Kalman filtering (to update the kinematic model) and an efficient neural network formulation (to update the dynamic model).
kinematic model for wheeled platform
In this section kinematic and dynamic model of four-wheel skid-steering mobile robot is presented. We refer to the real experimental construction consists of two-wheel differentially driven mobile robots namely MiniTracker 3 (see Fig.1) [9]. In order to simplify the mathematical model of SSMR we assume that [2] plane motion is considered only,This paper presents a kinematic extended Kalman filter (EKF) designed to estimate the location of track instantaneous centers of rotation (ICRs) and aid in model-based motion prediction of skid-steer robots.This methodology performs online calibration of vehicle kinematic models via Extended Kalman filtering and has been shown capable of calibrating deterministic and stochastic models of the forward, lateral, and angular slips for skid-steered robots. In this paper, we develop an analysis and experimental kinematic scheme for a skid-steering wheeled vehicle based-on a laser scanner sensor. The kinematics model is established based on the boundedness of the instantaneous centers of rotation (ICR) of treads on the 2D motion plane.
A survey and comparison of previous work on kinematic models for skid-steer mobile robots. Our results show that the friction-based kinematic model can successfully capture the dynamics of the robot to predict slippage, and hence provides more accurate pre-dictions of the robot’s motion when compared to the state-of-the-art on a real-world .
Based on the analysis of the kinematics of the skid-steered mobile robot, the underlying geometric and kinematic relationships between the wheel slips and locations of the instantaneous rotation centers are revealed.This article describes an improved kinematic model that takes these factors into account and verifies the model in a variety of working conditions, including different terrains and asymmetric loads, for two different wheeled skid-steered platforms.
The GPU implementation of the proposed method . GPs model skid-steer robot motion across varying terrains. The GP mean captures model residuals, accounting for . [13]S. Rabiee and J. Biswas, “A friction-based kinematic model for skid-steer wheeled mobile robots,” in 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). . This article describes an improved kinematic model that takes these factors into account and verifies the model in a variety of working conditions, including different terrains and asymmetric loads, for two different wheeled skid-steered platforms. It combines detailed slip and terramechanic-based dynamic models of wheel–terrain interaction with online learning via Extended Kalman filtering (to update the kinematic model) and an efficient neural network formulation (to update the dynamic model).In this section kinematic and dynamic model of four-wheel skid-steering mobile robot is presented. We refer to the real experimental construction consists of two-wheel differentially driven mobile robots namely MiniTracker 3 (see Fig.1) [9]. In order to simplify the mathematical model of SSMR we assume that [2] plane motion is considered only,
This paper presents a kinematic extended Kalman filter (EKF) designed to estimate the location of track instantaneous centers of rotation (ICRs) and aid in model-based motion prediction of skid-steer robots.This methodology performs online calibration of vehicle kinematic models via Extended Kalman filtering and has been shown capable of calibrating deterministic and stochastic models of the forward, lateral, and angular slips for skid-steered robots.
In this paper, we develop an analysis and experimental kinematic scheme for a skid-steering wheeled vehicle based-on a laser scanner sensor. The kinematics model is established based on the boundedness of the instantaneous centers of rotation (ICR) of treads on the 2D motion plane.A survey and comparison of previous work on kinematic models for skid-steer mobile robots. Our results show that the friction-based kinematic model can successfully capture the dynamics of the robot to predict slippage, and hence provides more accurate pre-dictions of the robot’s motion when compared to the state-of-the-art on a real-world . Based on the analysis of the kinematics of the skid-steered mobile robot, the underlying geometric and kinematic relationships between the wheel slips and locations of the instantaneous rotation centers are revealed.This article describes an improved kinematic model that takes these factors into account and verifies the model in a variety of working conditions, including different terrains and asymmetric loads, for two different wheeled skid-steered platforms.
Choosing the right excavator to dig your basement can be daunting, given the many options and sizes available. The best choice depends on factors like site accessibility and job specifics – in this case, digging a foundation area of around 40’x60’x10’.
implementation of skid steer kinematic model|wheeled kinematic model